by Charlotte Randall
 |
| (source: Guardian) |
On the 27th of June 2015, it was reported that a Belgian
woman had become the first to successfully conceive a child after having her
ovarian tissue, which had been removed and frozen when she was thirteen due to
sickle cell anaemia, transplanted back into her body.
Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder which causes a
base mutation on the coding strand of DNA in the genes that produce
haemoglobin, which results in the deformation of red blood cells, making them
become sickle shaped and unable to carry enough oxygen. The disorder can lead
to fatal complications such as strokes, pulmonary hypertension and kidney
dysfunction, which can lead to kidney failure.
Belgian doctors offered the woman in question a stem cell
transplant from one of her siblings, at age eleven; however, the procedure
involved intense chemotherapy in order to destroy the sickle cells, which would
inevitably damage her ovaries and make her infertile. She chose to have
fragments of her right ovary removed and frozen. Ten years on, these fragments
were grafted onto her left ovary and two years later she conceived a boy. This
has been considered a huge medical breakthrough for fertility, especially
concerning young women with cancer. This story got me thinking about other
critical fertility landmarks in the past decades and how they are affecting
society today.
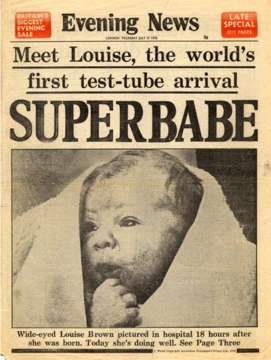
Test tube babies
On the 25th July, 1978, Louise Joy Brown, the first “test
tube” baby was born. The baby was the product of the first In Vitro
Fertilization (IVF) procedure, developed by gynaecologist Patrick Steptoe and
physiologist Robert Edwards (the latter won the Nobel Prize for Medicine in
2010). The basis of the IVF used with
Brown’s parents was the mother’s eggs collected from her fallopian tubes after
her natural ovulation. The sperm was then fused with the egg outside the womb,
dividing to form an embryo, which was then inserted into the uterus. The
procedure, although following the same steps, has quickly developed to make it
more likely that a foetus will develop and that many women in a high age range
can become pregnant, by using techniques such as Transvaginal Oocyte Retrieval,
which means many oocytes (immature egg cells can be removed), drugs for ovarian
hyperstimulation which have the aim to produce 2-7 eggs which can form embryos
and the injection of hormones such as progesterone in order to increase the
success rate of implantation.
In 2013 it was estimated that over 5 million people have
undergone IVF; however, the process doesn’t always work. According the NHS
website the success rates are:
•
32.2% for women under
35
•
27.7% for women aged
35-37
•
20.8% for women aged
38-39
•
13.6% for women aged
40-42
•
5% for women aged 43-44
•
1.9% for women aged over 44
Also, there have been considerable
ethical and social issues with the IVF procedure such as a religious view of
“playing God” and life beginning with conception and so throwing away embryos
not being implanted is murder. There are also medical risks such as multiple
births when more than one embryo is transferred back into the uterus, which can
lead to prematurity and pregnancy loss. Despite this, IVF has enabled millions
of infertile couples be able to have children when previously it had been impossible, changing
countless lives.
Three-Parent
Babies
On
the 24th of February of this year, the House of Lords passed an amendment to the
2008 Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act in order to allow a new and
controversial IVF technique, the aim of which is to prevent children being born
with serious mitochondrial diseases, by using two eggs and a sperm: i.e. two
mothers and a father. The process works by the DNA being removed from the donor
egg cell through a process called Maternal Spindle Transfer. The DNA from the
mother’s egg cell is removed and then is inserted into the donor egg. The rest
of the process is very similar to the above process of IVF where the egg is
fused with the sperm and is inserted into the uterus. This process has been encouraged
as it has shown that the hybrid egg can prevent the inheritance of
mitochondrial diseases as the genetic information that codes for the faulty
mitochondria from the mother is not inserted into the donor egg.
However,
this new procedure has caused great controversy, with The Human Genetics Alert claiming that it will “inevitably lead to
a future of “designer babies”.” There are also questions about the safety of
the procedure as it has not undergone any clinical trials yet and has only been
tested on primates, mice and human eggs that have not been implanted into a
uterus. Despite this, this procedure has serious potential to allow women with
genetic mitochondrial abnormalities to have children of their own.
Making
babies without men (or women)
A
concept that sounds impossible. It is commonly known that a baby can only be
“made” through a male and female. However, it is argued that this may change.
Research has shown that adult cells such as human skin cells as well as
fibroblasts, cells that build structures for tissues, may have the capability
to be programmed back to embryonic stem cells. This cell could then form either
a male or female gamete (i.e. egg or sperm) making sure it is it opposite of
the partner’s gender. Please note, however, I found very few scholarly articles
on this subject so most of this information was found through newspapers;
therefore, the accuracy of this information may not be strong. Indeed, it is
widely acknowledged that once a stem cell begins to differentiate to form a
specialised cell, it is committed to that path and can not change back.
However, with the rapid advancements in stem cell technology, this could be a
real possibility in the future. This would be another major advancement for
couples that are infertile and maybe lead to same-sex couples being able to
have children genetically similar to both parents. However, much more research
must be conducted before any firm conclusions are made.
Conclusion
Medical advancements in conception have made huge
cultural and scientific changes and will continue to do so by allowing millions
of infertile couples the opportunity to have children or to have children with
lower risks of disease. Despite the controversy, the procedures have brought
great happiness across the world. However, it has been questioned whether the
amount of money, time and research that goes into these procedures is truly
worth it. Of course, it is unfair that infertile couples cannot have children;
however, it is arguable that the resources might be better used elsewhere, for
example treating and researching diseases that affect millions alive today.
However, it is without a doubt that these advancements have revolutionized
reproduction forever and have changed, and will continue to change, millions of
lives.
Sources

Comments
Post a Comment
Comments with names are more likely to be published.